44
Vol. 66, No. 3 2015
Northeast Florida Medicine
Endovascular Neurosurgery
versus Systemic Thrombolysis for Acute Ischemic Stroke
(SYNTHESIS Expansion) and Mechanical Retrieval and
Recanalization of Stroke Clots using Embolectomy (MR
RESCUE).
5,6,7
These trials were largely criticized because
of flawed study design and the inability to answer whether
intra-arterial therapy with recanalization is beneficial for
large vessel occlusion. However, 2015 saw a paradigm shift in
the treatment of acute ischemic stroke with the publication
of five randomized clinical trials showing that endovascular
therapy is highly beneficial in patients with occlusion of the
intracranial internal carotid artery or middle cerebral artery
up to six hours after stroke onset (Figure 2).
2015 Clinical Trials Highlights:
MRCLEAN (Multicenter Randomized ClinicalTrial of Endo-
vascularTreatment for Acute Ischemic Stroke in theNetherlands)
8
• Eligible patients had confirmed large vessel occlusion in
the anterior circulation within six hours of stroke onset
• 500 patients enrolled at 16 medical centers (233 endo-
vascular therapy vs. 267 medical therapy alone)
• Absolute difference of 13.5percentage points (95percent
confidence interval, 5.9 to 21.1) in the rate of functional
independence (mRS 0 to 2) in favor of endovascular
intervention (32.6 percent vs. 19.1 percent)
• No significant difference in mortality or symptomatic
intracranial hemorrhage
EXTEND-IA (Extending the Time for Thrombolysis in Emer-
gency Deficits – Intra-Arterial)9
• Trial was stopped early because of efficacy of endovascular
therapy after 70 patients were enrolled in 12 medical
centers in Australia (35 endovascular therapy vs. 35
medical therapy)
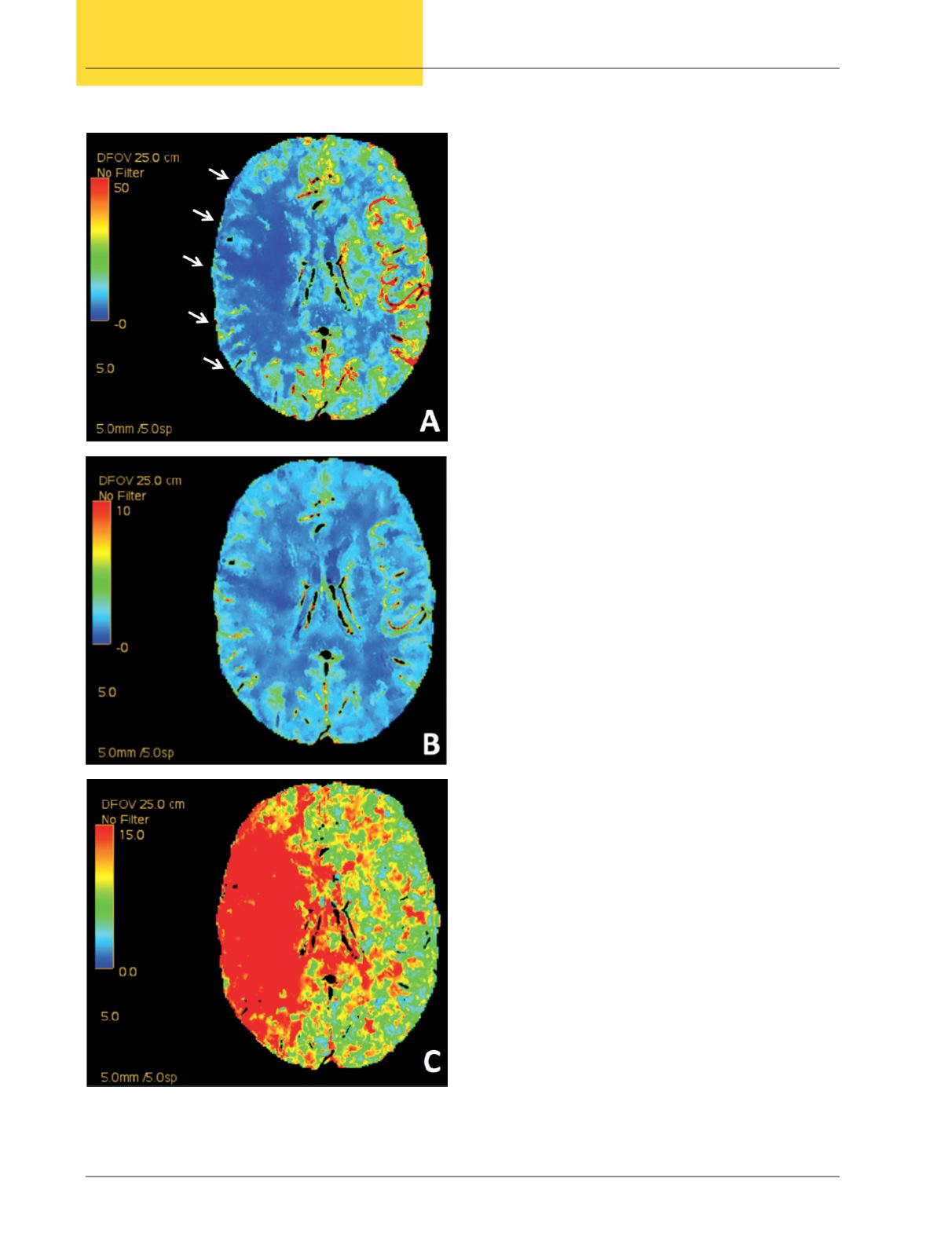
Figure 1.
Computed tomography perfusion (CTP) study.
Panel A shows cerebral blood flow (CBF), demonstrating an
area of flow mismatch between the hemispheres and decreased
blood flow in the region supplied by the right middle
cerebral artery (white arrows). Panel B shows cerebral blood
volume (CBV), depicting relatively symmetric hemispheres
with preserved blood volume despite decreased blood flow
(ischemic penumbra – salvageable tissue). Panel C shows mean
transit time (MTT), demonstrating decreased time in the area
supplied by the right middle cerebral artery (red hue).


